January 13, 2025 – The United Kingdom’s geographical landscape is ever-evolving, influenced by natural phenomena, climate change, and human activities. This comprehensive article delves into recent developments, challenges, and insights shaping the UK’s geography.
1. Climate Change and Its Impact on the UK
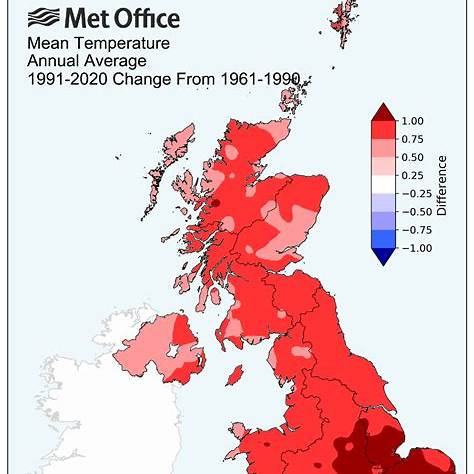
The UK’s climate is undergoing significant transformations due to global warming, affecting weather patterns, sea levels, and ecosystems.
1.1. Record-Breaking Temperatures
Recent data indicates that 2024 was the first year to surpass the 1.5°C global warming threshold, marking a critical point in climate change discussions.
1.2. Extreme Weather Events
The UK has experienced a series of extreme weather events, including Storm Bert in November 2024, which brought unprecedented rainfall and flooding to various regions.
2. Renewable Energy Milestones
The UK has made significant strides in renewable energy, with 2024 being a record year for wind power generation.
3. Biodiversity and Conservation Efforts
Research led by the University of Oxford’s School of Geography and the Environment has found that logged tropical forests still hold substantial value for biodiversity, emphasizing the importance of conservation efforts.
4. Educational Developments in Geography
The Geographical Association has highlighted the increasing relevance of geography in various career paths, noting that geographers are among the top 10 highest-paying jobs projected for 2025.
5. Geographical Publications and Resources
The January 2025 issue of Geographical Magazine offers in-depth articles on topics such as declining birth rates and their effects, as well as healing efforts in Ukraine amid ongoing conflict.
6. Urbanization and Infrastructure
The UK’s urban landscape continues to evolve, with significant investments in infrastructure aimed at enhancing connectivity and sustainability.
6.1. High-Speed Rail Developments
The expansion of high-speed rail networks, such as HS2, aims to reduce travel times between major cities, promoting economic growth and reducing regional disparities.
6.2. Smart Cities Initiatives
Cities like London and Manchester are implementing smart city technologies to improve urban living, focusing on efficient resource management and enhanced public services.
7. Coastal Erosion and Management
Coastal regions in the UK are facing challenges due to erosion, necessitating comprehensive management strategies to protect communities and ecosystems.
7.1. Erosion Hotspots
Areas such as the East Riding of Yorkshire are experiencing significant land loss, prompting authorities to implement coastal defense mechanisms.
7.2. Managed Retreat Strategies
In some regions, managed retreat is being considered as a sustainable approach to address the challenges posed by rising sea levels and erosion.
8. Agricultural Landscape and Food Security
The UK’s agricultural sector is adapting to changing climatic conditions, with a focus on sustainable practices to ensure food security.
8.1. Crop Diversification
Farmers are exploring diverse crop varieties that are resilient to changing weather patterns, aiming to maintain productivity and profitability.
8.2. Technological Integration
The adoption of precision agriculture technologies is enhancing efficiency and sustainability in farming practices across the UK.
9. Natural Hazards and Preparedness
The UK is enhancing its preparedness for natural hazards, including floods and storms, through improved forecasting and infrastructure resilience.
9.1. Flood Defense Systems
Investments in flood defense systems, such as the Thames Barrier, are crucial in protecting urban areas from potential flooding events.
9.2. Community Awareness Programs
Educational initiatives are being implemented to raise awareness about natural hazards and promote community preparedness.
10. Geopolitical Considerations
Geopolitical developments, including Brexit, continue to influence the UK’s geographical landscape, affecting trade routes, border management, and international relations.
10.1. Trade Route Realignments
Post-Brexit, the UK is establishing new trade agreements, necessitating adjustments in logistics and transportation networks.
10.2. Border Infrastructure
The establishment of new border controls has led to the development of infrastructure to manage the flow of goods and people efficiently.
Conclusion
The UK’s geography is characterized by dynamic changes influenced by environmental, technological, and geopolitical factors. Understanding these developments is essential for policymakers, educators, and the public to navigate the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.